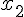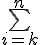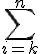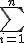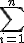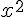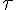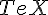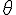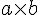Thursday, April 25, 2024, 12:41 AM
Site: Trinity Moodle
Course: Trinity Moodle (Home)
Glossary: Math Notation Help
S
square bracket |
square root@@@sqrt{x}@@@ is @@sqrt(x)@@ |
subscript |
sum (summation)
\symbolname_{lowerexpression}^{upperexpression}
$$\bigsum_{i=k}^{n}$$ gives and $$\sum_{i=k}^{n}$$ gives
$$\LARGE\bigsum_{\small{i=1}}^{\small{n}}$$ gives and $$\large\sum_{\small{i=1}}^{\small{n}}$$ gives |
superscript |
T
tau (lower case greek letter) |
TeX |
theta (lower case greek letter) |
Theta (upper case greek letter) |
times |
![\left[a,b\right] \left[a,b\right]](https://moodle.trinitydc.edu/filter/tex/pix.php/22be842f9527b4b0ef3b7085b5486b7b.gif)